by Per Fuchs, Steven Lockhart, and Gautam Varma.
In our Engineering Energizers Q&A series, we highlight the engineering minds driving innovation across Salesforce. Today, we meet Per Fuchs, a senior software engineer with the Hyper Database team. In close collaboration with others, his team empowers Data 360 to execute analytical queries directly on 100+ external systems.
Discover how the team transitioned from hand-built C++ SQL transformations to AI-assisted, configuration-driven dialects — rapidly expanding Zero Copy connector coverage and validating correctness with an automated 25,000-query testing workflow. This helped guarantee dependable advanced pushdown execution across SQL engines with diverse semantics while keeping test expectations automatically aligned to real remote-engine behavior.
What is your team’s mission building advanced pushdowns that enable Zero Copy in Data 360 to query across external data lakes via the Hyper Database?
Our mission empowers Data 360 to execute SQL queries directly on external database/data lakes. This approach eliminates the need for customers to move, duplicate, or restructure their data. Many organizations want to access their data directly from remote engines such as Snowflake, Redshift, and BigQuery, each implementing SQL uniquely. We built a optimization framework to convert Data 360 SQL into each engine’s native dialect, allowing Hyper to push computation as close to the data as possible. This process reduces network transfer, improves latency, and ensures segmentation, transformations, and activation workflows operate seamlessly, even when customer data remains entirely remote.
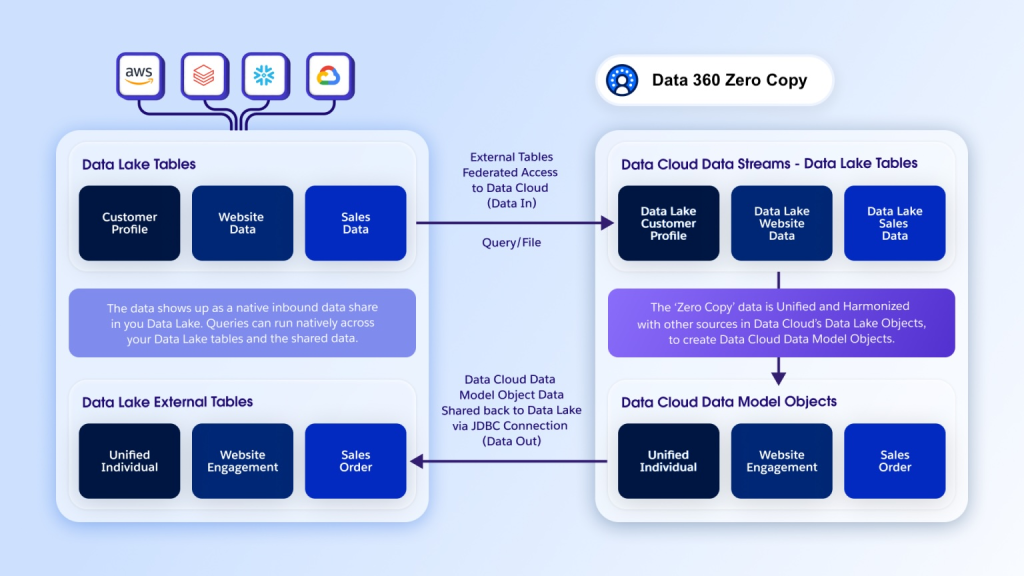
Virtualize and act in Data 360 without moving external data.
To ensure reliable pushdown, Hyper serves as the central optimization layer for Data 360 workloads — including segmentation, activation, transformations, and inference — not just dialect translation. Pushdown behavior needs to remain consistent across these application surfaces, even though each remote engine implements SQL differently. Ultimately, our goal is to let customers run analytical workloads directly on external systems with the same correctness and consistency they expect when executing locally in Data 360.
What engineering bottlenecks limited your ability to scale Hyper’s advanced pushdown support in Data 360 Zero Copy from 5 to 100+ connectors before adopting AI automation?
Before integrating AI automation, expanding Data 360’s Zero Copy support faced significant limitations in transforming Data 360 SQL into SQL for the new remotes. Each new connector demanded engineers review extensive documentation, interpret differences from Hyper semantics, design translation rules, and encode them directly in C++. This took 40 days of engineering work per dialect. This was due to the challenges of managing inconsistencies across SQL engines presented. While SQL appears standardized, each system shows differences in operator handling, function support, type coercion, precision handling, and error semantics. Engineers repeatedly rediscovered these nuances for each new dialect, slowing development and increasing error potential. The requirement for new C++ code paths and separate review cycles for every connector caused development costs to rise exponentially. At that time, we supported 5 connectors, and this model could not scale to the broader connector landscape that ultimately grew to more than 100.
Shifting to a JSON-based dialect configuration language removed the C++ bottleneck entirely. These configuration files typically have around 2000 lines.
How did AI help you tackle the challenge of generating 2000 lines of JSON config per dialect?
Configuring SQL dialects was once a laborious process. Each dialect configuration produced roughly 2,000 lines of JSON covering functions, operators, and type rules. Engineers manually reviewed SQL documentation for each remote system, deciphering language differences from DC-SQL, and then hand-coded roughly 2000 lines of JSON configuration per dialect. This involved extensive feature analysis, testing, error examination, and iterative refinement. Consistency across engines meant cross-referencing existing dialects for patterns and special cases, and ensuring the test execution resulted in a consistent behavior across different systems. This repetitive cycle of documentation lookups, pattern matching, and test-driven iteration consumed more than a month per engine.
Now, AI transforms this workflow. We provide the AI agent with the remote SQL reference, the JSON dialect specification, examples of existing dialects, and an ordered suite of tests for each dialect section. This ordered testing is crucial as it maps to different dialect sections and prevents regressions as the agent refines its work. The agent builds and refines the dialect a section at a time. interprets test failures, reads remote error messages and documentation, and leverages dialect inheritance and existing dialects for contextual hints. Engineers now focus on reviewing semantic gaps, rather than manual configuration. This AI-powered, test-driven workflow reduces dialect construction time from about 40 days to roughly 10 days per engine.
What validation challenges required your team to build a fully automated 25,000-query testing workflow to trust AI-generated SQL dialects?
Introducing AI-generated transformation presented a validation challenge. AI could produce syntactically correct but semantically inaccurate SQL, and manual review alone could not ensure correctness at scale. To address this, we developed an automated workflow that executes 25,000 functional SQL queries across Hyper and every remote engine. The workflow compares results across systems. It identifies mismatches and classifies them as expected differences, acceptable alternatives, or genuine correctness errors.
A critical element of this workflow is its feedback loop. Remote engine error messages and deviations feed directly back into the AI model. This allows the model to refine the dialect iteratively until it aligns with observed engine behavior. This closed-loop system ensures we validate translations based on real execution outcomes, rather than documentation alone.
Another key capability is that the testing workflow automatically updates expected results based on the remote engine’s real output. Engineers simply review the differences and correct only the behaviors they disagree with — typically a few root causes per system and affecting fewer than 20% of total test cases. This eliminates manual test maintenance and accelerates iteration dramatically.
Per shares why engineers should join Salesforce.
What measurable productivity gains did your team achieve by combining AI-generated SQL dialects with an automated testing workflow?
Combining AI-assisted dialect generation with automated validation accelerated our delivery cadence. The automated testing workflow amplified these gains. It gave the AI immediate execution feedback. The system highlights mismatches and allows the AI to refine translations autonomously. This removes the reliance on human reviewers to catch correctness issues. Engineers focus only on semantic gaps where AI lacks sufficient context. This enabled parallel development and faster iteration, representing a roughly 4× throughput improvement.
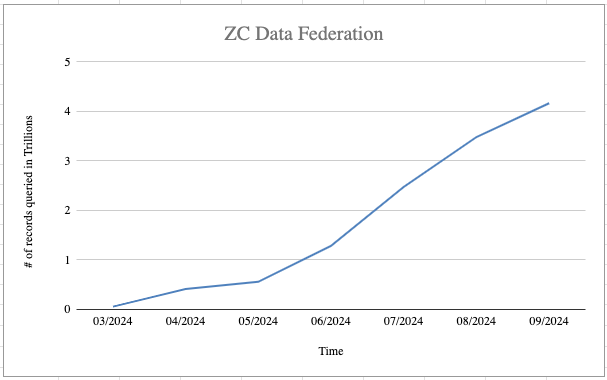
As a result, the Hyper team could drastically extend their support to 16 dialects within 3 months. This enabled Data 360 to expand Zero Copy connector support from 5 to more than 100 connectors. This expansion reflects a 20x increase in Zero Copy connector coverage. The shift enables Data 360 to push down analytical workloads into a broader range of external engines during query execution. It also maintains the reliability standards expected from Data 360.
Learn more
- Stay connected — join our Talent Community!
- Check out our Technology and Product teams to learn how you can get involved.